Resources
The World of the Sphere: Diagrams from De Sphaera Mundi
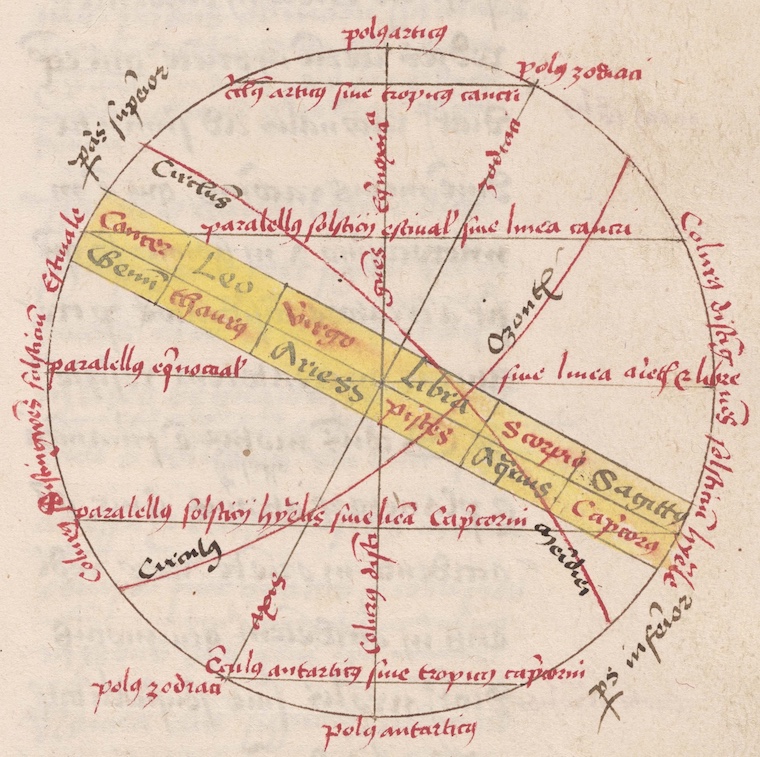
Interactive digital diagrams from UPenn MS Codex 1881 are available at aylinmalcolm.com/sacrobosco.
Manuscript Video Orientations: LJS 445 and LJS 497
Video orientations for other manuscripts are available on the Schoenberg Institute YouTube channel.
Online Sources and Tools
- Geoffrey Chaucer. A Treatise on the Astrolabe. Ed. F. N. Robinson (Internet Medieval Source Book, Paul Halsall, 1997). https://sourcebooks.fordham.edu/source/chaucer-astro.asp.
- Darin Hayton. An Introduction to the Astrolabe (2012). http://dhayton.haverford.edu/wp-content/uploads/2012/02/Astrolabes.pdf.
- The Museum of the History of Science, Oxford. The Astrolabe: An Online Resource (2006). http://www.mhs.ox.ac.uk/astrolabe.
- Richard Wymarc. The Astrolabe Project. http://www.astrolabeproject.com.
Further Reading
- Crofton Black, ed. Transformation of Knowledge: Early Manuscripts from the Collection of Lawrence J. Schoenberg (Paul Holberton Publishing, 2006).
- Elly Dekker. Illustrating the Phaenomena: Celestial Cartography in Antiquity and the Middle Ages (Oxford University Press, 2013).
- Edward Grant. Planets, Stars, and Orbs: The Medieval Cosmos, 1200-1687 (Cambridge University Press, 1996).
- Paul Kunitzsch. Stars and Numbers: Astronomy and Mathematics in the Medieval Arab and Western Worlds (Ashgate, 2004).
- James E. Morrison. The Astrolabe (Janus, 2007).
- John D. North. Cosmos: An Illustrated History of Astronomy and Cosmology (University of Chicago Press, 2008).
- Marijane Osborn. Time and the Astrolabe in the Canterbury Tales (University of Oklahoma Press, 2002).
- John M. Steele. A Brief Introduction to Astronomy in the Middle East (Saqi Books, 2008).